本文的应用是stanford corenlp多线程的使用,在对数据进行分词、词性标注和命名实体识别的过程数据量较大,处理时间较长,单线程已经不能满足需求。 这个使用场景是,读取文本,每一行是一个json类型的字符串,需要将其中部分文本进行词性标注等处理,然后再写到新的一个文件中(多线程读同一个文件,处理后,多线程写同一个文件)
- java 使用corenlp
java中的多线程
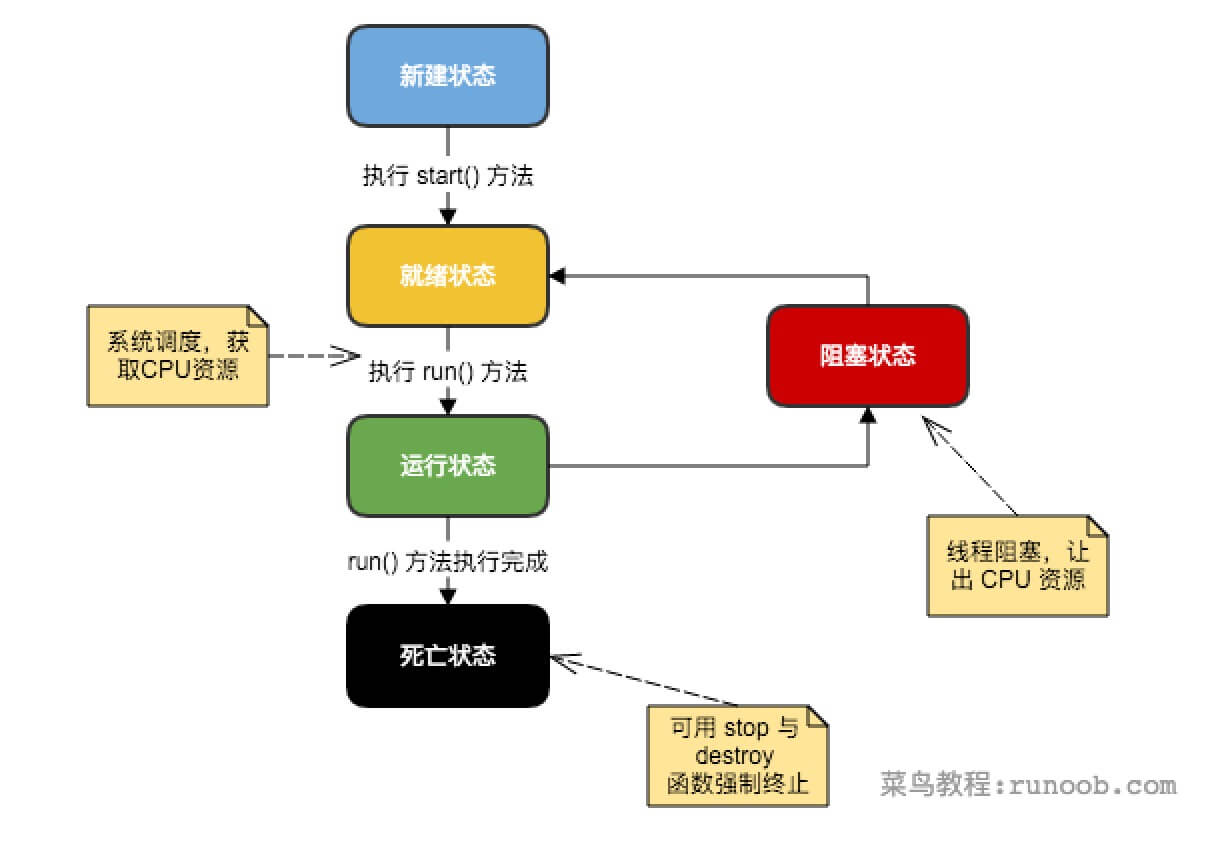
下图所示是一个线程的生命周期,在java中可以通过三种方法来创建线程:
1 通过实现Runnable接口
2 通过继承Thread类本身
3 通过Callable 和Future创建线程
具体可以参照 http://www.runoob.com/java/java-multithreading.html
 本文采用的是实现Runnable接口来实现ReadThread和WriterThread, 需要重写run方法。
本文采用的是实现Runnable接口来实现ReadThread和WriterThread, 需要重写run方法。
ReadThread 需要注意的是我们的需求是,多线程按行读取同一文件,所以在多个线程应该共享的是同一个BufferReader,这样才能保证不重复读取。
另一需求是,我们需要将各个ReadThread处理好的结果交给WriterThread去写到同一文件,我们需要一个队列,读线程不断的往这个队列中去写文件,写线程从中读取然后写到文件中。
BlockingQueue 这在java多线程中起着重大的作用,它解决了多线程中的数据共享问题。假如我们有若干的生产者线程,又有若干的消费者线程,如果生产者把准备好的数据共享给消费者,就可以利用该队列来传递数据。在本文的场景下,就是读线程把分词和词性标注好的数据交给写线程去写到文件中。
所谓阻塞,是在两种场景下,一种是当队列中没有数据的时候,一种是队列中数据已经满的时候,就会自动阻塞,但是该队列能够被自动唤醒。
可以参照 http://www.cnblogs.com/jackyuj/archive/2010/11/24/1886553.html 对该队列的详细介绍。
回到我们的应用场景中,为了实现数据共享,TheadReader和ThreadWriter应该是用的同一个BlockingQueue对象。
WriteThread 在WriteThread中 就是负责把从队列中取到的数据写入文件中。
实现中需要注意的细节, 在ReadThread中BufferReader不能在某个线程中关闭,这样会在其他中出现问题。
public class ReaderThread implements Runnable{
protected BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = null;
public static String filePath;
BufferedReader br = null;
Boolean is_train = true;
StanfordCoreNLP corenlp = new StanfordCoreNLP("StanfordCoreNLP-chinese.properties");
public ReaderThread(BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue,BufferedReader br){
this.blockingQueue = blockingQueue;
this.br = br;
}
public Map<String, List<String>> wordFeature(String text) {
Map<String, List<String>> features = new HashMap<>();
Annotation document = new Annotation(text);
corenlp.annotate(document);
List<String> res_tokens = new ArrayList<String>();
List<String> res_poss = new ArrayList<String>();
List<String> res_ners = new ArrayList<String>();
List<String> res_starts = new ArrayList<String>();
List<String> res_ends = new ArrayList<String>();
List<CoreMap> sentences = document.get(CoreAnnotations.SentencesAnnotation.class);
for(CoreMap sentence: sentences) {
List<CoreLabel> tokens = sentence.get(CoreAnnotations.TokensAnnotation.class);
for(CoreLabel token: tokens) {
String word = token.getString(TextAnnotation.class);
String pos = token.getString(PartOfSpeechAnnotation.class);
String ner = token.getString(NamedEntityTagAnnotation.class);
int start = token.beginPosition();
int end = token.endPosition();
res_tokens.add(word);
res_ners.add(ner);
res_poss.add(pos);
res_starts.add(start+"");
res_ends.add(end+"");
}
}
features.put("ners", res_ners);
features.put("poss", res_poss);
features.put("tokens", res_tokens);
features.put("starts", res_starts);
features.put("ends", res_ends);
//System.out.println(features);
return features;
}
@Override
public void run(){
try {
String buffer =null;
while((buffer=br.readLine())!=null){
buffer=buffer.replaceAll("\r|\n", "");
JSONObject jsonObj;
jsonObj = new JSONObject (buffer);
String query = jsonObj.getString("query");
query=BCConvert.qj2bj(query);
Map<String, List<String>> question_feature = wordFeature(query);
//中间省略,处理成你需要输出的格式,放到队列中
blockingQueue.put(out);
}
blockingQueue.put("EOF"); //When end of file has been reached
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch(InterruptedException e){
}catch(JSONException e) {
}//注意该部分 不能关闭流
}
}
//写线程
public class WriterThread implements Runnable{
protected BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = null;
private int count = 0;
private int threadsize = 0;
private String outfile;
public WriterThread(BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue, int threadsize, String outfile){
this.blockingQueue = blockingQueue;
this.threadsize = threadsize;
this.outfile = outfile;
}
@Override
public void run() {
PrintWriter writer = null;
try {
writer = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter( new FileOutputStream(outfile),"UTF-8"));
while(true){
String buffer = blockingQueue.take();
if(buffer.equals("EOF")){ //注意下什么时候写进程停止,根据场景本身修改下
// System.out.println("写出EOF");
count += 1;
if(count == this.threadsize) {
break;
}
continue;
}
writer.println(buffer);
System.out.println(buffer);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
writer.close();
}
}
}
- python使用corenlp
python多线程使用corenlp比java简单
python有封装好的corenlp服务,但是在使用的过程出现服务未终端,client老是连接超时的问题。
对该服务的使用不赘述了,可以参考 http://blog.csdn.net/guolindonggld/article/details/72795022
在python中多线程并非是真正的多线程,如果想要充分使用多核CPU资源,在python中大部分情况 需要使用多进程。python中有一个multiprocessing多进程包。
在我们的需求场景下,是需要多线程处理后输入到同一文件,因此在任务中需要一个回调函数,将处理后的结果返回
def mycallback(x):
result.write(str(x) + '\n')
python中采用线程池(pool),特别方便,只需要往池子里丢入需要处理的数据,告诉他处理的方法是什么,它就会给你返回结果。
lines = file.readLines()
pool_size = multiprocessing.cpu_count()
p = Pool(pool_size)
for line in lines:
p.apply_async(myFunction, (line,), callback=mycallback)
在myFunction中定义需要处理的方法就行,对corenlp的使用就可以放到这个函数中定义,将处理的结果返回即可。
以上是针对特定的应用场景,对比了java和python的多线程使用corenlp。